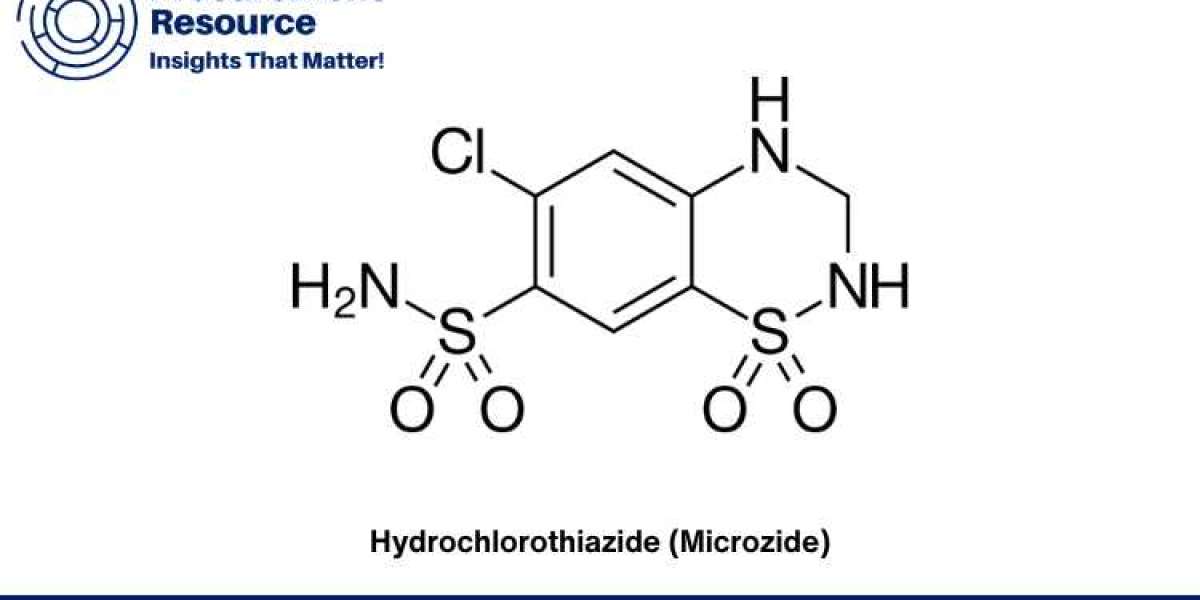
Hydrochlorothiazide, commonly known by its brand name Microzide, is a widely used diuretic medication. It is primarily prescribed to treat high blood pressure and swelling due to fluid build-up in the body. As a thiazide diuretic, Hydrochlorothiazide works by helping the kidneys to eliminate unneeded water and salt from the body through urine. The production of this essential drug involves several steps, from the procurement of raw materials to the final manufacturing process. This report delves into the intricacies of the Hydrochlorothiazide production process, examining each phase to provide a comprehensive understanding of its manufacturing and associated costs.
Manufacturing Report and Process
The manufacturing of Hydrochlorothiazide involves a series of meticulously controlled chemical reactions and purification steps to ensure the final product's efficacy and safety. The process can be broadly categorized into several key stages:
Request For Sample: https://www.procurementresource.com/production-cost-report-store/hydrochlorothiazide/request-sample
1. Synthesis of Hydrochlorothiazide
The production begins with the synthesis of the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API), Hydrochlorothiazide. This synthesis typically involves a multi-step chemical process starting from simple organic compounds. The primary steps include:
- Preparation of 3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid: This is the initial raw material, which undergoes several chemical transformations.
- Formation of the benzothiadiazine ring: Through a series of chemical reactions, including sulfonation and cyclization, the benzothiadiazine ring structure is formed, which is a critical component of Hydrochlorothiazide.
- Purification: The crude Hydrochlorothiazide is purified using crystallization or other suitable methods to ensure the removal of impurities and by-products.
2. Formulation
Once the API is synthesized and purified, the next step is formulating the medication into its final dosage form. This involves mixing the API with various excipients (inactive ingredients) to create the final product, whether it be a tablet, capsule, or liquid form. The formulation process includes:
- Mixing: The API is blended with excipients to ensure uniform distribution.
- Granulation: The mixture may undergo wet or dry granulation to improve its flow properties and compressibility.
- Compression: For tablet forms, the granulated mixture is compressed into tablets using a tablet press.
- Coating: Tablets may be coated to improve taste, stability, or appearance.
3. Quality Control
Quality control is an integral part of the manufacturing process. It involves rigorous testing of the raw materials, intermediate products, and final product to ensure they meet the required specifications and standards. Common tests include:
- Purity and potency testing: Using techniques like High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) to verify the concentration of Hydrochlorothiazide.
- Dissolution testing: Ensuring that the drug releases its active ingredient at the correct rate.
- Stability testing: Checking the product's stability under various environmental conditions.
Raw Material Costs
The cost of raw materials is a significant factor in the overall production cost of Hydrochlorothiazide. These costs can fluctuate based on several factors, including the availability of raw materials, market demand, and supplier pricing. Key raw materials involved in the production include:
1. Organic Chemicals
The synthesis of Hydrochlorothiazide requires various organic chemicals such as 3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid and other reagents used in the formation of the benzothiadiazine ring. The prices of these chemicals can vary depending on their purity, availability, and the scale of purchase.
2. Excipients
Excipients, although not the active component, play a crucial role in the formulation of the final product. Common excipients include:
- Binders: Such as microcrystalline cellulose.
- Fillers: Such as lactose or starch.
- Disintegrants: Such as croscarmellose sodium.
- Lubricants: Such as magnesium stearate.
The cost of excipients can also impact the overall production cost, though they are generally less expensive compared to the active ingredients.
3. Packaging Materials
Packaging is another essential component that adds to the cost. This includes the cost of bottles, blister packs, labels, and boxes. Packaging costs can vary based on the type and quality of materials used, as well as the complexity of the packaging design.
Latest News
The pharmaceutical industry is constantly evolving, with new developments and trends impacting the production and cost dynamics of medications like Hydrochlorothiazide. Here are some of the latest updates relevant to its production:
1. Supply Chain Disruptions
The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly impacted global supply chains, causing disruptions in the availability of raw materials and increasing production costs. Manufacturers have had to navigate these challenges by seeking alternative suppliers or adjusting production schedules.
2. Technological Advancements
Advancements in pharmaceutical manufacturing technologies are continually improving the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of drug production. Innovations in continuous manufacturing, for example, are being adopted to streamline the production process and reduce waste.
3. Regulatory Changes
Regulatory changes can also impact production costs. For instance, stricter regulations on manufacturing practices or changes in drug approval processes can lead to increased compliance costs. Keeping abreast of these changes is crucial for manufacturers to maintain compliance and manage costs effectively.
4. Market Trends
The demand for Hydrochlorothiazide and similar medications can fluctuate based on market trends. Factors such as changes in prescribing patterns, the introduction of generic alternatives, or shifts in healthcare policies can influence the market dynamics and, consequently, the production costs.
5. Environmental and Sustainability Initiatives
There is a growing emphasis on sustainability in pharmaceutical manufacturing. Companies are increasingly adopting eco-friendly practices to reduce their environmental footprint. This includes measures like minimizing waste, optimizing energy use, and sourcing sustainable raw materials. While these initiatives may entail initial costs, they can lead to long-term savings and benefits.
Conclusion
The production of Hydrochlorothiazide (Microzide) is a complex process involving multiple stages, from raw material synthesis to final formulation and quality control. The costs associated with its production are influenced by various factors, including raw material prices, technological advancements, regulatory changes, and market trends. Keeping abreast of the latest developments and adopting efficient manufacturing practices are essential for managing production costs and ensuring the continued availability of this vital medication.