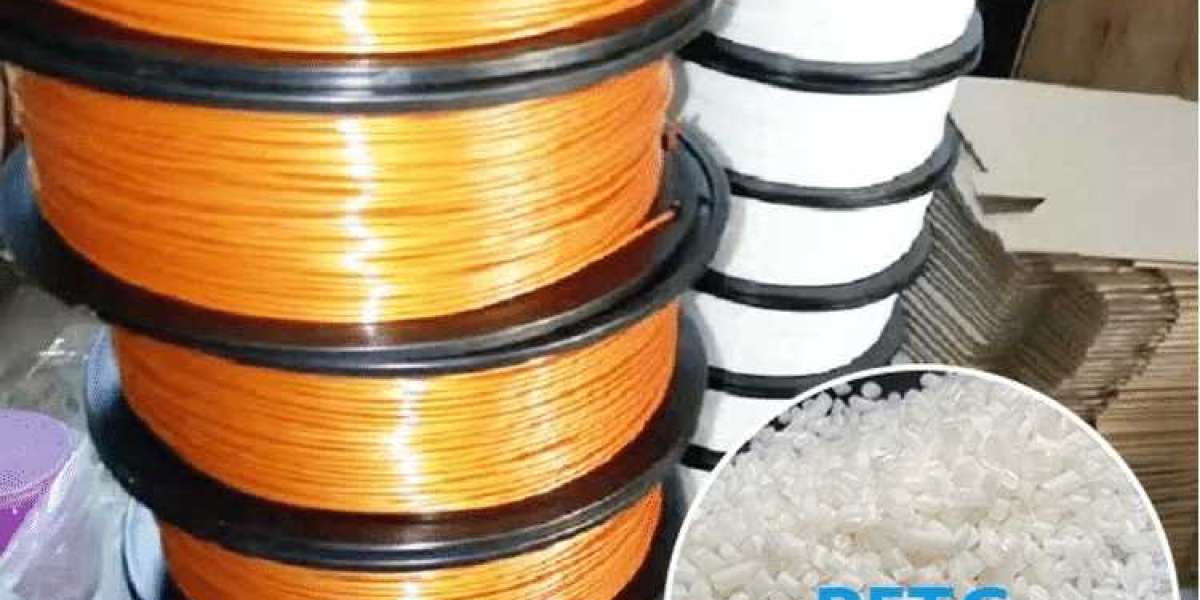
However, like all thermoplastics, PETG filament can experience shrinkage during the printing and cooling processes, leading to dimensional inaccuracies, warping, and reduced structural integrity. Fortunately, there are ways to minimize this issue, ensuring high-quality prints that meet your desired specifications.
What Causes PETG Filament Shrinkage?
PETG shrinkage occurs due to the material contracting as it cools after being extruded. When heated, thermoplastics like PETG expand, and when they cool down, they contract. This shrinkage can lead to warping or a poor fit in parts that require tight tolerances. Several factors contribute to shrinkage, including print settings, environmental conditions, and the filament's inherent properties.
Compared to materials like ABS, PETG generally has low shrinkage rates, but the problem can still arise, especially when printing large objects or using improper settings. The key to reducing PETG shrinkage is controlling the cooling process, optimizing print settings, and using appropriate printing surfaces.
Strategies for Reducing PETG Filament Shrinkage
Optimize Print Temperature and Cooling Settings
The temperature of the extruder plays a significant role in minimizing PETG shrinkage. PETG generally prints best between 230°C and 250°C. If the temperature is too high, the filament may stay molten for longer, causing it to contract more drastically as it cools. Finding the right temperature for your specific filament formulation is crucial to reducing shrinkage.
Equally important is controlling the cooling rate. PETG benefits from gradual, controlled cooling to prevent sudden contraction. It is recommended to use a cooling fan at low speeds (around 30-50%), which will help the layers solidify slowly and reduce the risk of warping.
Increase Bed Adhesion and Use a Heated Bed
A common cause of shrinkage-related warping is poor bed adhesion, especially in the early layers of a print. A heated bed is essential for PETG to combat this. Set your bed temperature between 70°C and 90°C, depending on the size of your print and the properties of your PETG filament.
To further improve adhesion, use a surface like a PEI sheet, painter's tape, or apply a thin layer of glue stick to the print bed. These surfaces help PETG stick firmly, preventing lifting at the edges, which can lead to shrinkage-related warping.
Adjust Part Design and Orientation
When designing parts for 3D printing, keep in mind the potential for shrinkage and warping, especially in large flat surfaces or intricate geometries. Where possible, avoid sharp corners and incorporate rounded edges into your designs. Sharp angles and flat surfaces tend to exacerbate warping and shrinkage, while curves distribute stress more evenly as the part cools.
Additionally, orient the part on the print bed in a way that minimizes large flat areas directly in contact with the bed. Vertical or diagonal orientation can help reduce the surface area prone to warping, thus minimizing shrinkage.
Manage Environmental Conditions
The environment in which you print can significantly affect PETG’s cooling behavior. Sudden changes in temperature, drafts, or cold air can cause uneven cooling, leading to increased shrinkage and warping. If possible, print PETG in an enclosed 3D printer or in a room with stable temperature and low airflow. This helps maintain a more controlled and consistent environment during the printing process.
Use Optimized PETG Filament Formulations
Many filament manufacturers have optimized PETG formulations designed to reduce shrinkage and warping. These filaments may include additives that enhance dimensional stability or reduce the material’s tendency to contract. If shrinkage continues to be an issue, consider experimenting with different brands of PETG to find one that works best for your specific needs.
PETG is a versatile filament that offers excellent printability and strength, but shrinkage can sometimes affect print quality. By optimizing your print settings, improving bed adhesion, adjusting part design, managing environmental conditions, and using advanced PETG formulations, you can effectively reduce shrinkage and ensure accurate, high-quality prints. With careful attention to detail and best practices, PETG’s shrinkage issues can be mitigated, allowing you to fully take advantage of its impressive properties.